
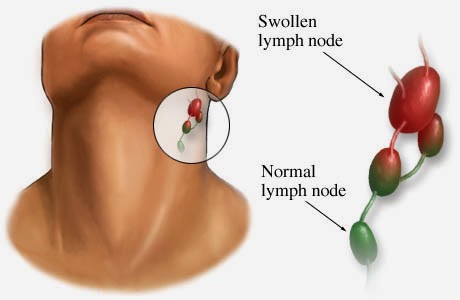
- CANCER PICTURES OF SWOLLEN LYMPH NODES IN ARMPIT SKIN
- CANCER PICTURES OF SWOLLEN LYMPH NODES IN ARMPIT FREE
Most studies of cancer cell metastasis in people have focused on cells circulating in the blood.
Comparing Metastatic Melanoma Cells in Lymph Versus Blood The study was supported in part by NCI’s Patient-Derived Models of Cancer program, which promotes the development of animal models that more closely mirror how tumor cells behave in humans. The team also used a second mouse model created by transplanting mouse melanoma cells into mice with normal immune systems.Ĭomparing these two mouse models let the researchers control for potential effects of the immune system on the spread of melanoma, Dr. These mice were used to avoid having the transplanted human cells seen as foreign and attacked by the immune system.
CANCER PICTURES OF SWOLLEN LYMPH NODES IN ARMPIT SKIN
However, precisely how oxidative stress kills circulating melanoma cells was not known.įor their studies, the team used a mouse model of metastasis created by transplanting melanoma cells from humans beneath the skin of specially bred mice with weakened immune systems.
CANCER PICTURES OF SWOLLEN LYMPH NODES IN ARMPIT FREE
Oxidative stress-an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body-causes chemical reactions that can damage proteins, DNA, and lipids (fats) in cells and disrupt normal cell processes. Morrison’s team found previously that one factor limiting the survival of melanoma cells circulating in the blood is that the cells experience a high level of oxidative stress. Metastasis is a highly inefficient process in that “the vast majority of cancer cells that try to migrate die before they ever have an opportunity to form a tumor,” Dr. Mouse Models Mimic Metastasis of Human Melanoma However, further work is needed before such drugs could be tested in people with melanoma, Dr. “This knowledge uncovers tremendous therapeutic potential, since enhancers and inhibitors of ferroptosis are being developed,” said Konstantin Salnikow, Ph.D., of NCI’s Division of Cancer Biology, who was not involved in the study. In studies in mice, a team led by Sean Morrison, Ph.D., director of the Children’s Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern, found that melanoma cells that travel through the lymphatic system are more resistant to a form of cell death called ferroptosis. The study, published September 3 in Nature, shows that melanoma cells that pass through the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream spread and form new tumors more readily than cells that directly enter the bloodstream. Now, an NCI-funded study may provide some answers, raising the possibility of new treatment approaches that could help keep melanoma from spreading, or metastasizing, the study investigators said. But the implications of this detour through the lymph nodes have remained unclear. Melanoma, the most aggressive form of skin cancer, is often incurable once the cancer has spread from the original site of the tumor to distant organs and tissues.ĭoctors have known for decades that melanoma and many other cancer types tend to spread first into nearby lymph nodes before entering the blood and traveling to distant parts of the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
